આ કુટુંબ Nepticulidae જાણીતા નાના શલભ કેટલાક પકડી, 3-8mm પાંખ-ટોચ પરથી પાંખ-ટોચ સુધીના. સરખામણી માટે હું ઉપર બે શલભ તસવીર છે: સૌથી જાણીતા – Coscinocera hercules that tips the scales at nearly 9 ઇંચ, અને નાના એક (yes that tiny little speck below the Hercules moth) – Ectoedemia rubifoliella, also imaged below. The Nepticulidae are surprisingly diverse, પર સાથે 800 species described that likely represent only 10% of the actual diversity (Powell, 2009). In the United States we have only 80 પ્રજાતિઓ, જે 25 are known from the west. When you compare that diversity to the 100 or so species known from Great Britain, it’s clear that the US knowledge is vastly lacking. ખરેખર, પર 80% of all nepticulid diversity is known from Europe alone. A strange inversion when you consider that the neotropics are the world’s most diverse ecosystems yet have only 74 known Nepticulidae species! (Puplesis, 2000). Why is this so?
 Ectoedemia rubifoliella 3.3મી.મી.
Ectoedemia rubifoliella 3.3મી.મી.
 Stigmella ostryaefoliella 3.1મી.મી.
Stigmella ostryaefoliella 3.1મી.મી.
The European diversity can easily be explained away due to a high concentration of bored Lepidopterists. The Holarctic fauna is not the most diverse and it therefore has become the best understood on the planet, not to mention they have had a long history of gentleman entomologists dating back hundreds of years. But the rest of the Nepticulidae diversity remains a mystery because they are really, ખરેખર નાના, hard to spread, and difficult to identify as adults! I have actually had little practice or success with mounting Nepticulidae, and the above specimens should be credited to Dr. ડેવ વેજનર. The very few that I do have in my collection are simply pinned and un-spread; and even the pinning proves hard enough when a slip of the hand can obliterate the entire specimen. Apparently the best method for mounting is to knock them down in the freezer and pin them while they are still alive. Not the most humane, but the only way to keep the moth from drying before your eyes and becoming impossible to manipulate. As hard as the adults are to manage, the larvae are rather characteristic in that most are leaf miners – they feed on the material વચ્ચે the leaf epidermises. This lends to the common name of “leaf blotch miners” because you can see the translucent patches the moths have ‘mined’ out from inside the leaf. Not only is each species rather host-specific, but they tend to form very characteristic mine patterns within the leaf. So if you find a leaf mine and you know the species of plant, chances are you can find out the species of Nepticulid within it (however not all leaf mines are nepticulids, there are lots of other insects that do this as well). Rearing these moths are also rather simple, all you have to do is pop the leaf in a bag and wait for the moth to finish feeding. One caterpillar only needs one leaf (or tiny section of leaf) – but care has to be taken to keep the leaf green while the caterpillar feeds. If the leaf dies, so will the caterpillar. Because of this paradoxical ability to identify the mines and not the adults there is a surprising amount of ecological research done on them, especially since a few pose threats to commercial crops. The first image below clearly illustrates the caterpillar feeding within the leaf – and the trail of frass it has left behind.
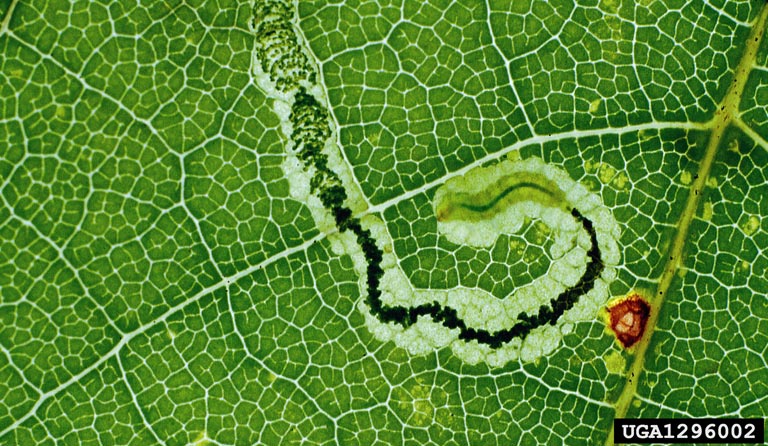 Stigmella aceris (link to image credit)
Stigmella aceris (link to image credit)
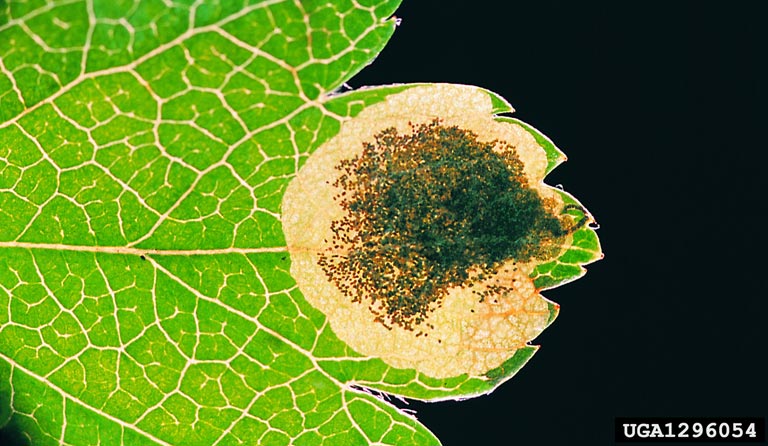 Stigmella paradoxa (link to image credit)
Stigmella paradoxa (link to image credit)
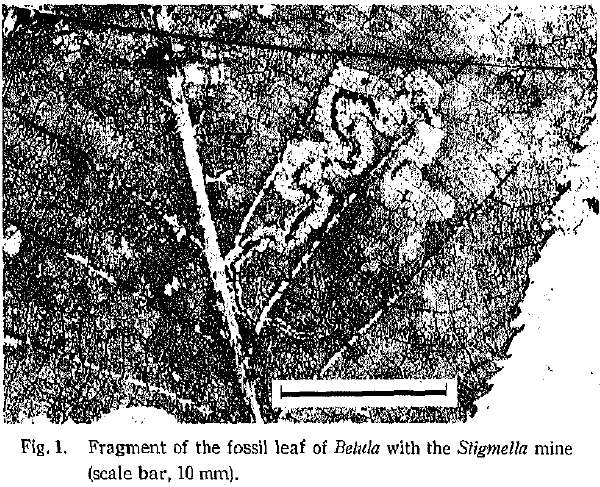
If you look at the above images of mines it’s not all that difficult to imagine structures like this fossilizing. And amazingly, they have! The first image below (Labandeira et al., 1994) shows a variety of leaf mining Nepticulidae mines (and a Gracillariidae) from the mid-Cretaceous (97 મિલિયન વર્ષ પહેલાં). The spectacular thing about leaf mines is that you can get down to genus level and sometimes even species. The authors were able to differentiate between the nepticulid genera સ્ટિગ Mella અને Ectoedemia based on the patterns preserved in the fossils; patterns we still use to help separate genera today. The bottom illustration is from a mine discovered in Japan that is only around 8 million years old (Kuroko, 1987).
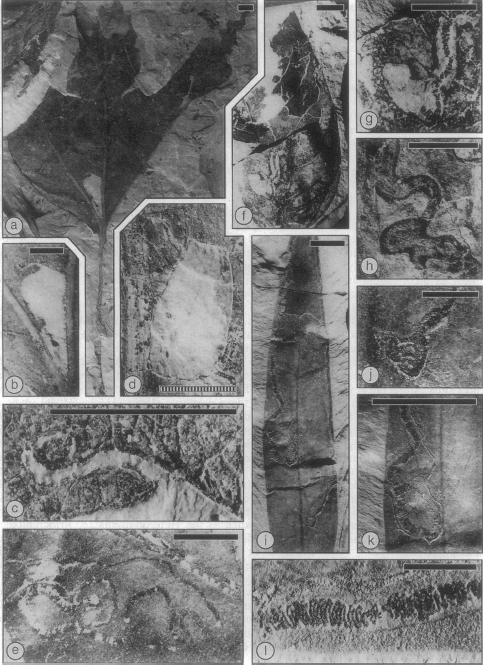 (Labanderia, 1994)
(Labanderia, 1994)
સંદર્ભ
Kuroko, H. (1987). A Fossil Leaf Mine of Nepticulidae (લેપિડોપ્ટેરા) from Japan. Bulletin Sugadaira Montane Res. Cen., No.8, 119-121.
Labandeira, સી. (1994). Ninety-Seven Million Years of Angiosperm-Insect Association: Paleobiological Insights into the Meaning of Coevolution Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 91 (25), 12278-12282 ડી.ઓ.આઇ.: 10.1073/pnas.91.25.12278
PUPLESIS, R., DIŠKUS, A., ROBINSON, G., & ONORE, જી. (2002). A review and checklist of the Neotropical Nepticulidae (લેપિડોપ્ટેરા) Bulletin of The Natural History Museum. Entomology Series, 71 (01) ડી.ઓ.આઇ.: 10.1017/S0968045402000032
Powell, J.A., Opler, P.A. (2010). પશ્ચિમ ઉત્તર અમેરિકાના શલભ – by J. એક. Powell and P. એક. Opler Systematic Entomology, 35 (2), 347-347 ડી.ઓ.આઇ.: 10.1111/j.1365-3113.2010.00525.x


રસપ્રદ!
I will give these critters a go when the season starts. As a dipterist specializing in the Psychodidae, the Nepticulids’ size range is slightly above what I am usually working with. I suspect that I can make the transition rather rapidly if I just modify my current methods slightly…
Happy to encourage someone to start working with leps! I think the scales on the microleps are more sensitive than would be on a Psychodidae, but I do know how delicate those wings are on the flies so they might not be that far apart after all.
There are numerous Nepticuliids in Monterey County, કેલિફોર્નિયા, from the following families (અત્યાર સુધી!) Sumac,Barberry,Birch,Pea,Beech,Walnut,
Mallow,Sycamore,Knotweed,Buckthorn,Rose,Willow. Some plants have more than one species. Rosa californica has an Ectoedemia and two Stigmellas. રસપ્રદ, pretty moths.
ક્રિસ,
I am making a video about microlepidoptera moths for school. I would like to use your picture of the microlepidoptera compared to the huge Coscinocera hercules for a video we are making. May I please use it?
આભાર,
Cesar
ખાતરી, you’re welcome to use the image for school!
ક્રિસ,
Thank you for letting us use your picture we will send you the link to the movie when it’s done.
આભાર,
Cesar
[…] શલભ ઓફ tiniest […]